No products in the cart.
Crypto, Events, Technology
Demystifying Blockchain
Cryptocurrency and blockchain have quickly become a global phenomenon and hot topic in the business world and investing community. Known by most people, but understood by few. Cryptocurrency, an abbreviation of cryptographic currency, is a type of digital asset that uses blockchain technology. Benefits of blockchain include improves efficiency; reduces the cost of maintaining and reconciling ledgers; and provides certainty on ownership and history of assets. Understanding this new technology is the first step to understanding the importance of blockchain for companies and their clients.

Cryptocurrency, Blockchain and Bitcoin
The first implementation of a blockchain was invented in conjunction with Bitcoin in 2009. Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency, a type of digital currency that is secured against fraud and theft by means of mathematical encryption algorithms. The creator of Bitcoin and its specific form of blockchain technology was an unknown person going by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. In his white paper, he described the value of blockchain as follows: “Using digital signatures, hashing, and proof of work to avoid double spending and fraud, the Bitcoin blockchain enables its participants to confidently transfer value using math for validation and verification instead of a trusted third party.”
The Bitcoin blockchain solved the third party problem other cryptographers could not fix: the Bitcoin blockchain cryptographically links blocks of transactions together and creates an incentive mechanism that rewards participants who supplied the computing power to link the blocks, thus making it unfeasible to change the ledger. A common error is to equate all blockchain technologies to the Bitcoin blockchain. Newer, next generation blockchains, not associated with Bitcoin, do not necessarily share all the attributes of the Bitcoin blockchain. However, without Bitcoin, there would be no blockchain technology of any sort. Therefore, the better you understand Bitcoin, the better you will be able to understand how other cryptocurrencies and blockchains work.
Core Components of Blockchains
A blockchain consists of four core components: the ledger; the peer-to-peer network; the consensus mechanism; and the incentive mechanism.
A blockchain is a ledger of transactions, each of which records a change in ownership of the native currency of a particular blockchain. For example, Bitcoin is the native currency of the Bitcoin blockchain. All transactions are grouped into a block, added to the blockchain and linked to all the previous blocks with cryptography. Cryptography is the math used to prove no data has been changed, which is the basis for an immutable blockchain.
The peer-to-peer network consists of a large number of nodes (computers) that update and store the complete synchronized version of the blockchain. Every node in the network agrees on one state of the blockchain at any point in time. Therefore, it is possible for anyone to independently verify a transaction. The network distributes security among thousands of computers making it unfeasible for malicious actors to compromise the network. As there is a large number of nodes, a node can go offline without affecting the network. This is the value proposition of decentralization.
The combination of a blockchain and a peer-to-peer network is not inherently immutable, secure or reliable. The consensus mechanism makes those attributes possible due to the combination of a consensus protocol and consensus algorithms. Consensus is a process in which nodes agree on one version/state of a blockchain without knowing or trusting the other nodes.
The Bitcoin blockchain does not require permission; anyone can participate as a node, a developer or an end-user. Bitcoin, including other blockchains, is a self-organizing army of participants and volunteers. There has to be a mechanism to incentivize the participants who invest capital to secure the network. Bitcoin is the incentive. The two most common consensus algorithms and their respective incentive mechanisms are proof of work and proof of stake. Proof of work is the Bitcoin consensus algorithm. The proof of work algorithm mints new Bitcoin into existence for every winning number and the Bitcoin becomes part of the fixed monetary supply. This is the incentive that motivates an army of people to voluntarily participate in the Bitcoin blockchain and other public blockchains.
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Security
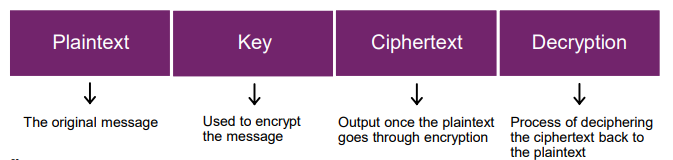
To secure cryptocurrency and blockchain transactions, cryptography and encryption are used. As was previously mentioned, cryptography is the math used to prove no data has been changed which is the basis for an immutable blockchain. Cryptography is also seen as the science of secret communication. Encryption is the process of creating a secret and the code to make the secret information accessible to those that should have access. An encrypted message is called a cipher-text. To be able to read the secret message, the receiver should have a “key” to decrypt the cipher-text.
Blockchains are secure, however the byproduct of a secure ledger means security is pushed out to the end-users. Therefore, cryptocurrency users have complete custody, responsibility and control of their assets, unlike traditional assets that rely on management by third party financial institutions. The plus-side is that users will have 100% custody of their assets, however the downside is that they are also a 100% responsible for their own security.
There are three main enemies of cryptocurrency security: external hackers; “the enemy within”; and carelessness. External hackers are a known threat with their malware, keylogging, phishing and social engineering. But a lesser known danger is “the enemy within”. This danger consists of trusted employees that exploit week security practices. Examples of carelessness are not backing up a private key, overall poor security practices and not making use of two-factor authentication.
Two-factor authentication, also known as 2FA, is the easiest and cheapest security measure with the highest return. 2FA is typically generated by an app that sends a six-digit code which expires in 20 seconds to your mobile device or desktop. The code is needed to access an account after entering usernames and passwords. If someone hacked your username and password, the hacker still couldn’t access your account without the 2FA code. This is an additional layer of security for logging into websites and sending cryptocurrency transactions.
Blockchain Use in Society
The application of blockchain has already impacted and improved real-world scenarios. Every day around the world, farmers harvest food products for global shipments. Sensors, which transmit data that is securely written to a blockchain, allow all participants in the supply chain to know the status of these shipments. As all data is recorded on a blockchain, the bankers, insurers, logistics companies and any others involved in the supply chain process will save time and money by knowing the latest information about the shipment. Since the blockchain ensures the accuracy of the data, these participants can budget and prepare for their part in the supply chain process more quickly and avoid costly errors along the way. Automated records on the blockchain tied to RFID (radio frequency identification) and other tracking software provides a secure and transparent way that allows all involved parties from origin to shipping to destination be aware of specific details on the shipment. Due to the use of blockchain, the entire process is sped up, has fewer errors and is more cost-effective, an advantage for suppliers, distributers, and customers.
Blockchain and Beyond Seminar – Learning programs that take your business forward
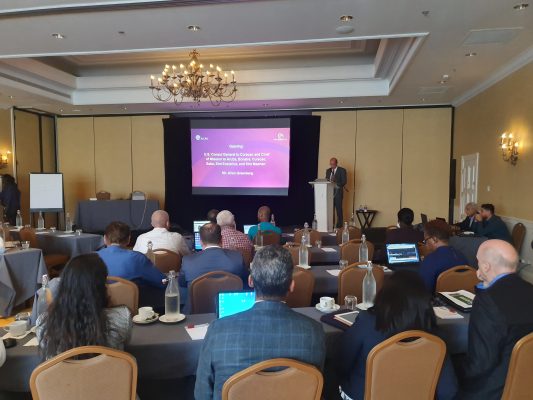

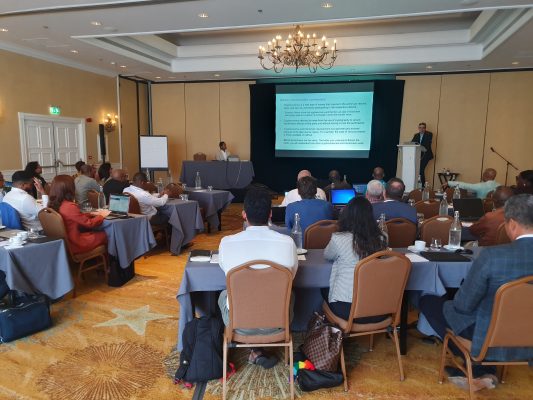
The American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) and Wall Street Blockchain Alliance work together to define the impact of blockchain technology for the accounting profession and advance the interests of both the public and profession in this area. On December 9th and 10th 2019, Global International Management LLC organized the AICPA and CIMA event “Demystifying Blockchain – Blockchain Fundamentals for Accounting and Finance Professionals Certificate” at the Curacao Marriot Beach Resort. The event was officially opened by U.S. Consul General to Curacao Mr. Allen Greenberg.
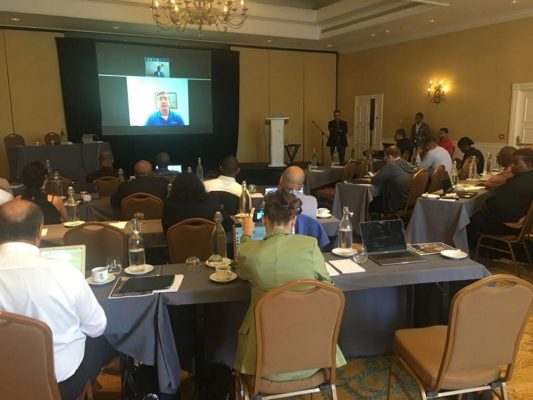

The event consisted of two full days of learning the blockchain fundamentals led by blockchain expert Kirk Phillips CPA, CMA, CFE, CPB, moderated by Rocher Cyrus CPA, CGMA, Managing Director of Global International Management LLC with additional interviews from recognized professionals in the field Andries Verschelden CPA and Dr. Sean Stein Smith DBA, CPA. The following topics were highlighted during the event:
- Learn about blockchain and crypto asset technology
- Identify the benefits and opportunities of blockchain
- Recognize the potential risks and challenges of technology adoption
- Regulatory concerns
- Blockchain trends

For more information about this or upcoming events, please visit the website of Global International Management LLC https://globalintmanagement.com/.
Writer: Nathasja JT Plaizier



